3.3 输出
1. write(chunk)
将chunk数据写到输出缓冲区。如我们在之前的示例代码中写的:
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("hello itcast!")
想一想,可不可以在同一个处理方法中多次使用write方法?
下面的代码会出现什么效果?
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("hello itcast 1!")
self.write("hello itcast 2!")
self.write("hello itcast 3!")
write方法是写到缓冲区的,我们可以像写文件一样多次使用write方法不断追加响应内容,最终所有写到缓冲区的内容一起作为本次请求的响应输出。
想一想,如何利用write方法写json数据?
import json
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
stu = {
"name":"zhangsan",
"age":24,
"gender":1,
}
stu_json = json.dumps(stu)
self.write(stu_json)
实际上,我们可以不用自己手动去做json序列化,当write方法检测到我们传入的chunk参数是字典类型后,会自动帮我们转换为json字符串。
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
stu = {
"name":"zhangsan",
"age":24,
"gender":1,
}
self.write(stu)
两种方式有什么差异?
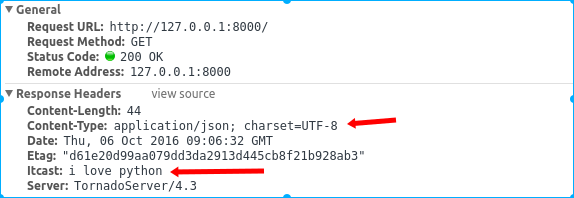
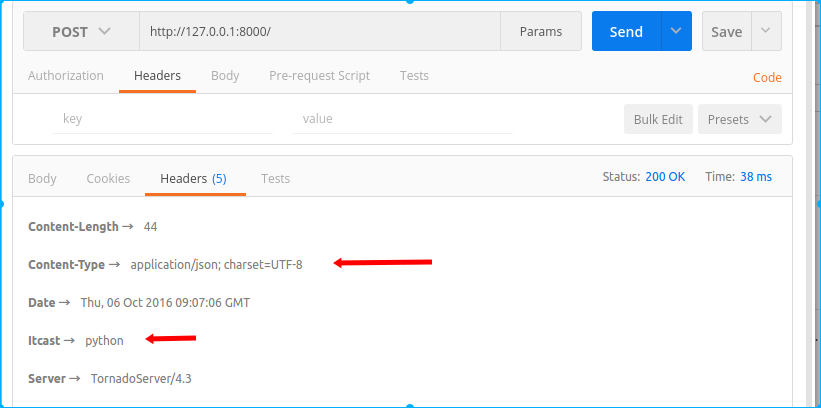
对比一下两种方式的响应头header中Content-Type字段,自己手动序列化时为Content-Type:text/html; charset=UTF-8,而采用write方法时为Content-Type:application/json; charset=UTF-8。
write方法除了帮我们将字典转换为json字符串之外,还帮我们将Content-Type设置为application/json; charset=UTF-8。
2. set_header(name, value)
利用set_header(name, value)方法,可以手动设置一个名为name、值为value的响应头header字段。
用set_header方法来完成上面write所做的工作。
import json
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
stu = {
"name":"zhangsan",
"age":24,
"gender":1,
}
stu_json = json.dumps(stu)
self.write(stu_json)
self.set_header("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8")
3. set_default_headers()
该方法会在进入HTTP处理方法前先被调用,可以重写此方法来预先设置默认的headers。注意:在HTTP处理方法中使用set_header()方法会覆盖掉在set_default_headers()方法中设置的同名header。
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def set_default_headers(self):
print "执行了set_default_headers()"
# 设置get与post方式的默认响应体格式为json
self.set_header("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8")
# 设置一个名为itcast、值为python的header
self.set_header("itcast", "python")
def get(self):
print "执行了get()"
stu = {
"name":"zhangsan",
"age":24,
"gender":1,
}
stu_json = json.dumps(stu)
self.write(stu_json)
self.set_header("itcast", "i love python") # 注意此处重写了header中的itcast字段
def post(self):
print "执行了post()"
stu = {
"name":"zhangsan",
"age":24,
"gender":1,
}
stu_json = json.dumps(stu)
self.write(stu_json)
终端中打印出的执行顺序:
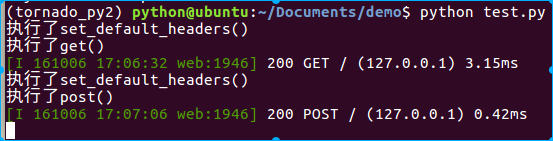
get请求方式的响应header:
post请求方式的响应header:
4. set_status(status_code, reason=None)
为响应设置状态码。
参数说明:
- status_code int类型,状态码,若reason为None,则状态码必须为下表中的。
- reason string类型,描述状态码的词组,若为None,则会被自动填充为下表中的内容。
| Code | Enum Name | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | CONTINUE | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.2.1 |
| 101 | SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.2.2 |
| 102 | PROCESSING | WebDAV RFC 2518, Section 10.1 |
| 200 | OK | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.3.1 |
| 201 | CREATED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.3.2 |
| 202 | ACCEPTED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.3.3 |
| 203 | NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.3.4 |
| 204 | NO_CONTENT | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.3.5 |
| 205 | RESET_CONTENT | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.3.6 |
| 206 | PARTIAL_CONTENT | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7233, Section 4.1 |
| 207 | MULTI_STATUS | WebDAV RFC 4918, Section 11.1 |
| 208 | ALREADY_REPORTED | WebDAV Binding Extensions RFC 5842, Section 7.1 (Experimental) |
| 226 | IM_USED | Delta Encoding in HTTP RFC 3229, Section 10.4.1 |
| 300 | MULTIPLE_CHOICES | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.4.1 |
| 301 | MOVED_PERMANENTLY | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.4.2 |
| 302 | FOUND | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.4.3 |
| 303 | SEE_OTHER | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.4.4 |
| 304 | NOT_MODIFIED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7232, Section 4.1 |
| 305 | USE_PROXY | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.4.5 |
| 307 | TEMPORARY_REDIRECT | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.4.7 |
| 308 | PERMANENT_REDIRECT | Permanent Redirect RFC 7238, Section 3 (Experimental) |
| 400 | BAD_REQUEST | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.1 |
| 401 | UNAUTHORIZED | HTTP/1.1 Authentication RFC 7235, Section 3.1 |
| 402 | PAYMENT_REQUIRED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.2 |
| 403 | FORBIDDEN | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.3 |
| 404 | NOT_FOUND | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.4 |
| 405 | METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.5 |
| 406 | NOT_ACCEPTABLE | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.6 |
| 407 | PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED | HTTP/1.1 Authentication RFC 7235, Section 3.2 |
| 408 | REQUEST_TIMEOUT | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.7 |
| 409 | CONFLICT | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.8 |
| 410 | GONE | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.9 |
| 411 | LENGTH_REQUIRED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.10 |
| 412 | PRECONDITION_FAILED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7232, Section 4.2 |
| 413 | REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.11 |
| 414 | REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.12 |
| 415 | UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.13 |
| 416 | REQUEST_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE | HTTP/1.1 Range Requests RFC 7233, Section 4.4 |
| 417 | EXPECTATION_FAILED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.14 |
| 422 | UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY | WebDAV RFC 4918, Section 11.2 |
| 423 | LOCKED | WebDAV RFC 4918, Section 11.3 |
| 424 | FAILED_DEPENDENCY | WebDAV RFC 4918, Section 11.4 |
| 426 | UPGRADE_REQUIRED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.5.15 |
| 428 | PRECONDITION_REQUIRED | Additional HTTP Status Codes RFC 6585 |
| 429 | TOO_MANY_REQUESTS | Additional HTTP Status Codes RFC 6585 |
| 431 | REQUEST_HEADER_FIELDS_TOO_LARGE Additional | HTTP Status Codes RFC 6585 |
| 500 | INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.6.1 |
| 501 | NOT_IMPLEMENTED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.6.2 |
| 502 | BAD_GATEWAY | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.6.3 |
| 503 | SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.6.4 |
| 504 | GATEWAY_TIMEOUT | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.6.5 |
| 505 | HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED | HTTP/1.1 RFC 7231, Section 6.6.6 |
| 506 | VARIANT_ALSO_NEGOTIATES | Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP RFC 2295, Section 8.1 (Experimental) |
| 507 | INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE | WebDAV RFC 4918, Section 11.5 |
| 508 | LOOP_DETECTED | WebDAV Binding Extensions RFC 5842, Section 7.2 (Experimental) |
| 510 | NOT_EXTENDED | An HTTP Extension Framework RFC 2774, Section 7 (Experimental) |
| 511 | NETWORK_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED | Additional HTTP Status Codes RFC 6585, Section 6 |
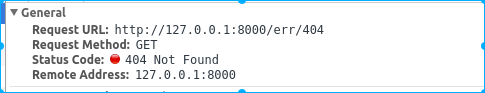
class Err404Handler(RequestHandler):
"""对应/err/404"""
def get(self):
self.write("hello itcast")
self.set_status(404) # 标准状态码,不用设置reason
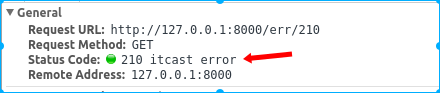
class Err210Handler(RequestHandler):
"""对应/err/210"""
def get(self):
self.write("hello itcast")
self.set_status(210, "itcast error") # 非标准状态码,设置了reason
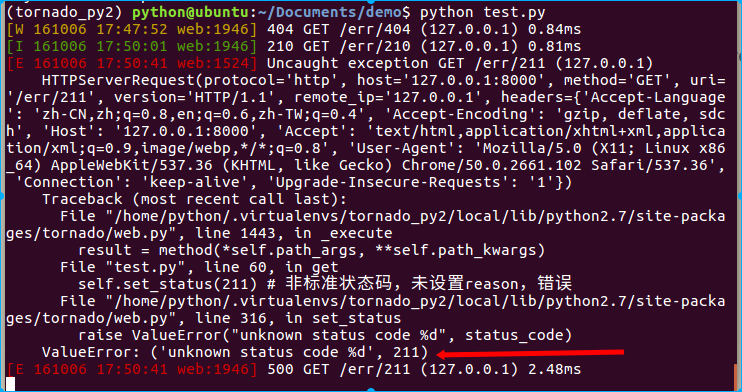
class Err211Handler(RequestHandler):
"""对应/err/211"""
def get(self):
self.write("hello itcast")
self.set_status(211) # 非标准状态码,未设置reason,错误
5. redirect(url)
告知浏览器跳转到url。
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
"""对应/"""
def get(self):
self.write("主页")
class LoginHandler(RequestHandler):
"""对应/login"""
def get(self):
self.write('<form method="post"><input type="submit" value="登陆"></form>')
def post(self):
self.redirect("/")
6. send_error(status_code=500, **kwargs)
抛出HTTP错误状态码status_code,默认为500,kwargs为可变命名参数。使用send_error抛出错误后tornado会调用write_error()方法进行处理,并返回给浏览器处理后的错误页面。
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("主页")
self.send_error(404, content="出现404错误")
注意:默认的write\_error()方法不会处理send\_error抛出的kwargs参数,即上面的代码中content="出现404错误"是没有意义的。
尝试下面的代码会出现什么问题?
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("主页")
self.send_error(404, content="出现404错误")
self.write("结束") # 我们在send_error再次向输出缓冲区写内容
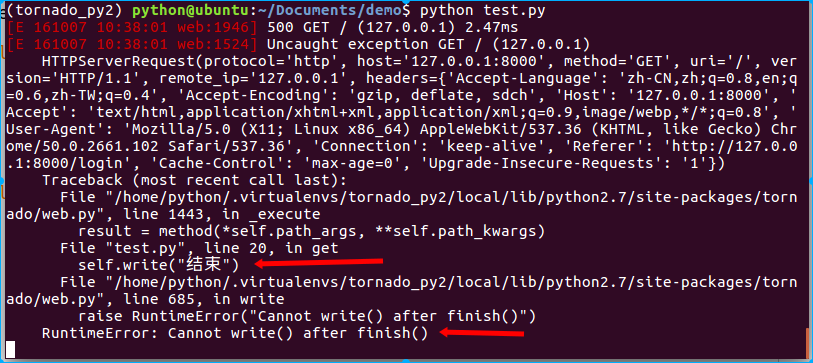
注意:使用send_error()方法后就不要再向输出缓冲区写内容了!
7. write_error(status_code, **kwargs)
用来处理send_error抛出的错误信息并返回给浏览器错误信息页面。可以重写此方法来定制自己的错误显示页面。
class IndexHandler(RequestHandler):
def get(self):
err_code = self.get_argument("code", None) # 注意返回的是unicode字符串,下同
err_title = self.get_argument("title", "")
err_content = self.get_argument("content", "")
if err_code:
self.send_error(err_code, title=err_title, content=err_content)
else:
self.write("主页")
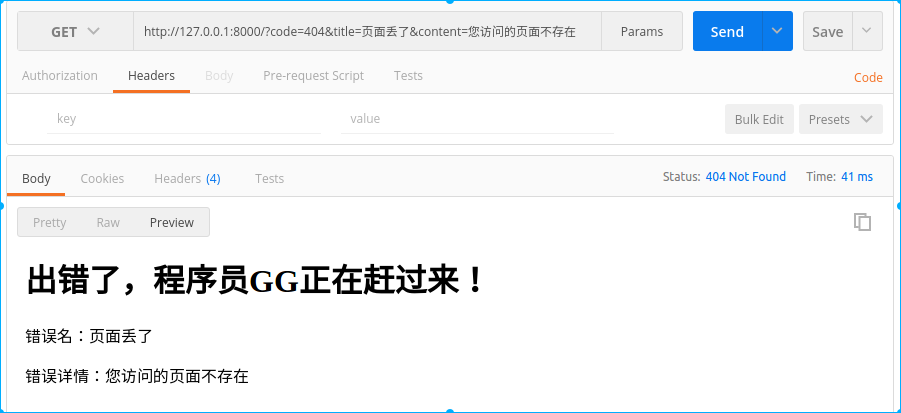
def write_error(self, status_code, **kwargs):
self.write(u"<h1>出错了,程序员GG正在赶过来!</h1>")
self.write(u"<p>错误名:%s</p>" % kwargs["title"])
self.write(u"<p>错误详情:%s</p>" % kwargs["content"])